RELATIONS WITH THE EU
The European Union and the United Nations
The EU is a staunch supporter of the UN. Cooperation between the EU and the UN system, including the UN Secretariat and the various UN Agencies, Funds and Programmes, spans all policy areas.
UN General Assembly
The UN General Assembly (UNGA) is comprised of all 193 Members of the United Nations and its work is carried out by six Main Committees and subsidiary organs
The General Assembly is the UN’s main deliberative, policymaking and representative organ.
Since 2011, the EU is an observer member with enhanced status at the UN General Assembly. This allows the EU to present common positions, make interventions, present proposals and participate in the general debate each September.
The added value of the EU is to coordinate among its 27 Member States to present a unified position. The EU coordinates its voting within the UN General Assembly’s six main committees, as well as other bodies and agencies such as the Economic and Social Council.
UN Security Council
The Security Council has primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security. It has 15 Members, and each Member has one vote
Article 34 of the Lisbon Treaty stipulates that EU members at the UN Security Council must act in concert and foster the interests of the EU. The strong presence of EU Member States at the UN Security Council and an effective coordination among them as well as with other partners contributes to the promotion of EU interests in a cooperative way.
In January 2025, Denmark and Greece will begin two-year terms as non-permanent members of the UN Security Council, joining Slovenia, which completes its term at the end of 2025. France is the only EU Member State with a permanent seat on the Security Council.
Supporting the UN
The EU and its Member States are the largest financial donors to the UN system
The EU and its Member States are collectively the single largest financial contributor to the UN system. Together, EU and its Member States provide one-quarter of all financial contributions to the UN’s funds and programmes, whilst EU Member States also provide almost one-third of the UN’s regular budget. For the three-year period from 2022-24, EU Member States account for 23.5% of the UN Peacekeeping budget.
Aligned with the UN’s 2030 Agenda and its Sustainable Development Goals, the EU and its Member States are the leading development donors in the world, providing €95.9 billion in development assistance in 2023, which accounts for 42% of global assistance. Much of this funding is channeled through UN agencies.
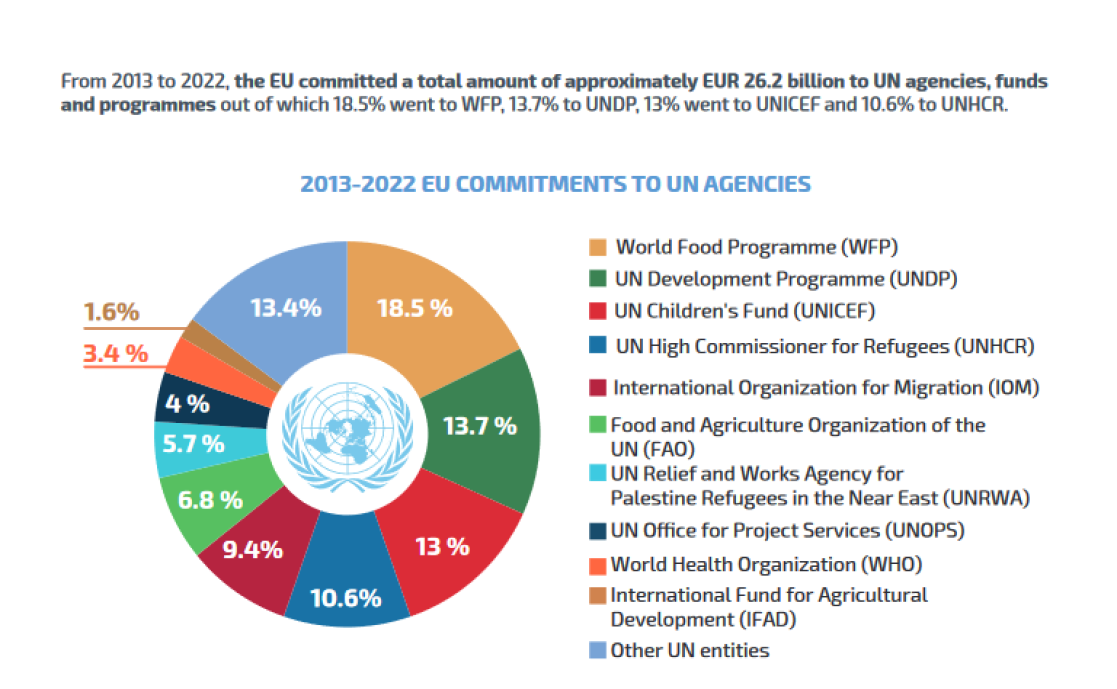
The EU and EU Member States are the top financial donors to many key UN bodies, including the World Health Organisation (WHO), the UN Development Programme (UNDP) and the UN’s Children Fund (UNICEF). The EU and EU Member States are the largest donors to the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA), providing overall financing over time of between 40-50%, representing a lifeline for this agency over the years.
Together, the EU and the UN work to eradicate hunger around the world. The EU and its Member States collectively fund 40% of the World Food Programme budget.
European Union
EU priorities at the UN General Assembly
Every year, the Council of the EU adopts EU priorities for the UN and the UN General Assembly, taking into account the UN's agenda and global issues. These priorities guide the EU's work for the year to come.
The Council adopted the EU priorities for the UN and the 79th session of the UNGA (September 2024 – September 2025) in June 2024.
The conclusions renew the EU’s determination to promote multilateral solutions based on the UN Charter, and back the UN Secretary General’s drive for 'peace in all its dimensions' and call for international cooperation to that end.
In the context of the grave, triple planetary crisis of climate change, biodiversity loss and pollution, which poses a global and existential threat and aggravates existing security concerns, the EU is committed to working with partners to accelerate a global, just and inclusive green transition. The EU is also determined to accelerate efforts to deliver the 2030 Agenda and achieve the Sustainable Development Goals, and looks forward to the Summit of the Future as a critical milestone for the multilateral system.
The EU will continue working on strengthening respect, protection, and fulfilment of all human rights and to call on all States to fully engage with the UN human rights system.
EU action at the UN in the coming year will be guided by the following overarching priorities:
I. Recommit to the foundations of a rules-based international order
II. Support international peace and security
III. Advance sustainable development and financing for development
IV. Address the triple planetary crisis
V. Foster trust through a more effective multilateral system
Furthermore, the EU will advocate for the meaningful participation of an independent, rights-based, diverse civil society in multilateral processes, including but not limited to human rights fora, peace mediation and decision-making process.

